29 March 2006 -- Total Solar
Eclipse (TSE2006)
Glenn Schneider, Steward
Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson Arizona 85721 USA
(updated 15 March 2006)
(updated 15 March 2006)
If the weather co-operates on 26 March 2006, TSE 2006 will be observed from Side, Turkey:
PRIMARY
SITE
Latitude = 36 47 15 N, Longitude = 31 22 38.7 E
Duration of Totality = 3m 50.4s
Latitude = 36 47 15 N, Longitude = 31 22 38.7 E
Duration of Totality = 3m 50.4s
| CONTACT |
UT |
Alt |
Az |
Pang |
Vang |
| First |
09 38 19.6 |
56.3 |
171 |
227 |
126 |
| Second |
10 54 53.7 |
54.3 |
204 |
49 |
330 |
| Mid-Eclipse |
10 56 48.9 |
54.1 |
205 |
N/A |
63 |
| Third |
10 58 44.2 |
54.0 |
206 |
226 |
156 |
| Last |
12 13 28.9 |
44.6 |
231 |
49 |
348 |
Our currently selected primary observing site is on centerline (middle of three blue lines on the map below) of the path of totality on the southern coast of Turkey on the Gulf of Antalya near Selimiye. The region is serviced by the Antalya International Airport, which itself is in within the path of totality. The southern coastal road traverses the path from northern to southern limit. Our site, LOCATED ON THIS SATELLITE PHOTOGRAPH, is on the grounds of the Sunrise Queen Hotel in the town of Side.
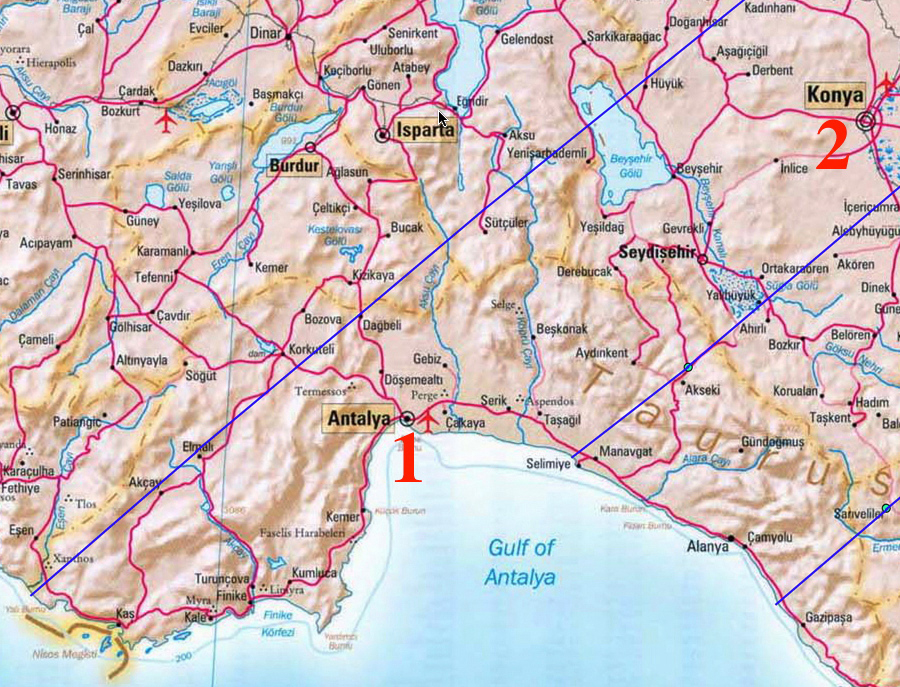
If the local weather threatens the eclipse observations, but is likely to be predictably better elsewhere with high certainty, we will relocate elsewhere in the path of totality by vehicle, or by air if a larger distance needs to be traveled to secure clear skies. If there is a high degree of expectation of cloud-cover over the path of totality (in Turkey) with little likelihood of success from the ground we will use the aircraft to observe TSE2006 from the air (above the clouds).
A. Air Contingency #1: Relocation
Six airfields have been identified within the path of totality (highlighted in green) with sufficient infrastructures to potentially allow "last minute" repositioning to observe TSE2006. Unfortunately, one of those, TOKAT, will be out of service. On an earlier posted page, the duration of totality at each of airfields (and circumstances for others outside of the path) are listed. The operational status and avialability/suitability of those individual airfields should be investigated (consult NOTAMS and other sources) if anyone is planning to use them.
Presumptively basing in (or near) Antalya, FLIGHT DISTANCES (One-Way) From (1) ANTALYA AIRPORT (LTAI) to the five other highlighted sights are given below:
km mi nM
(1) ANTALYA: 0 0 0
(2) KONYA: 197 122 106
(3) NEVSEHIR: 387 240 209
(4) KAYSERI: 462 287 250
(5) TOKAT: 614 381 332 (expected to be closed)
(6) SIVAS: 622 387 336
Click on the airfield names (above) for satellite images.
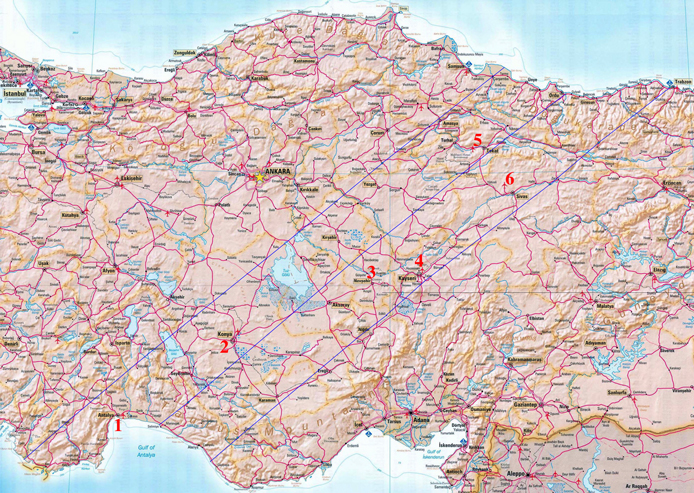
Path of Totality Across Turkey - Airfields in the Path of Totality.
Click on Map to View at FULL SIZE.
B. Air Contingency #2: Observations over Turkey
To observe the total phase of the
eclipse from the air, an aircraft must:
(1) be located at the center of the Moon's shadow as the shadow passes over the aircraft , and
(2) the aircraft must be flying a heading to permit viewing the eclipse out of the cabin windows.
Details computing and optimizing fight plans for airborne eclipse observations are discussed in conjunction with the EFLIGHT S/W here, which has been updated for TSE 2006.
Elaborating a bot on these two points:
1. The location path of the eclipse varies with altitude above sea-level, but is readily computable. As examples, the latitude and longitude of the CENTERLINE of the path of totality are tabulated as functions of time (UTC = GMT) in following tables for flight elevations of 32,000 ft to 44,000 ft in 2000 ft increments and time steps of 10 seconds along the entire path of totality over Turkey:
DIRECTORY of CENTERLINE FILES:
In addition to time, latitude, and longitude these files give the Duration of Totality (in seconds as would be seen from a STATIONARY observer, i.e., before correcting for the motion of an aircraft), The width of the shadow in kilometers, and the Altitude and Azimuth of the Sun at mid eclipse)
2. The aircraft must be flying on a heading to intercept the Moon's shadow at a specific location on centerline (for a given flight altitude) at the corresponding time. The aircraft heading must be equal (or very close) to the azimuth of the Sun (at mid eclipse) minus 90 degrees (i.e., so the aircraft has a velocity component in the direction of motion of the Moon' shadow, not against it).
Additionally:
3. To enable image acquisition by on-board observers, the aircraft must be flying on that heading to achieve an appropriate mid-eclipse intercept sufficiently ahead of second contact Here, for planning purposes in this specific case, the "totality run" is defined to start at mid-eclipse minus minutes, and will "break off" at mid-eclipse plus 4 minutes (permitting appx 2 minutes of post CIII viewing of the Sun as well).
(1) be located at the center of the Moon's shadow as the shadow passes over the aircraft , and
(2) the aircraft must be flying a heading to permit viewing the eclipse out of the cabin windows.
Details computing and optimizing fight plans for airborne eclipse observations are discussed in conjunction with the EFLIGHT S/W here, which has been updated for TSE 2006.
Elaborating a bot on these two points:
1. The location path of the eclipse varies with altitude above sea-level, but is readily computable. As examples, the latitude and longitude of the CENTERLINE of the path of totality are tabulated as functions of time (UTC = GMT) in following tables for flight elevations of 32,000 ft to 44,000 ft in 2000 ft increments and time steps of 10 seconds along the entire path of totality over Turkey:
DIRECTORY of CENTERLINE FILES:
In addition to time, latitude, and longitude these files give the Duration of Totality (in seconds as would be seen from a STATIONARY observer, i.e., before correcting for the motion of an aircraft), The width of the shadow in kilometers, and the Altitude and Azimuth of the Sun at mid eclipse)
2. The aircraft must be flying on a heading to intercept the Moon's shadow at a specific location on centerline (for a given flight altitude) at the corresponding time. The aircraft heading must be equal (or very close) to the azimuth of the Sun (at mid eclipse) minus 90 degrees (i.e., so the aircraft has a velocity component in the direction of motion of the Moon' shadow, not against it).
Additionally:
3. To enable image acquisition by on-board observers, the aircraft must be flying on that heading to achieve an appropriate mid-eclipse intercept sufficiently ahead of second contact Here, for planning purposes in this specific case, the "totality run" is defined to start at mid-eclipse minus minutes, and will "break off" at mid-eclipse plus 4 minutes (permitting appx 2 minutes of post CIII viewing of the Sun as well).
Baseline planning is predicated
upon following assumptions, which may be somewhat different in actual
detail or implementation:
A) Use of Raytheon Hawker-400 jet aircraft or similar:
- Climb to altitude: 18 minutes
- Cruise 450 kt (833 km/hr)
- Service Ceiling: 45,000 ft.
- PAX complement: 8 persons each
- Sunside windows: 5 (sharing necessary)
B) T/O and Landing from Antalya, Turkey (Int'l Airport)
- Lat = 36d 54' N, 30d 48' E
C) Total flight time T/O to Landing = 1 hour
A Eclipse flight "BASELINE" Scenario
Executable, with 40,000 ft observation, in 1 hour flying-time, from/to Antalya airport.
Baseline Scenario for Mid-Eclipse Intercept:
i) Flight Altitude = 40,000 ft*
ii) U.T. of mid-Eclipse Intercept = 10:57:50 U.T.
iii) Cruise speed = 450kt
It must be noted that the altitude of the Sun (angular degrees above the horizon) is 53.6 degrees at this location. This SHOULD be observable out the aircraft windows with some neck craning (but needs to be confirmed), in straight and level flight, BUT it would be highly desirable if the aircraft could be banked (tilted) - while still flying on a fixed heading - by whatever amount may be accommodated to "lower" the sun as seen through the aircraft windows. An intercept point chosen later in time (further to the North East) would have the Sun at a somewhat lower altitude - at the expense of additional flying time. For this baseline scenario, a 10:57:50 UT intercept is considered because of the short flight distance. Clearly, that can be adjusted. Note that 1 minute of flying time (not U.T. intercept)- parallel to the centerline of the path of totality - (after reaching altitude and nominal cruise speed) would move the intercept point by appx 7.5 nautical miles along the path of totality.
The baseline plan assumes a "no wind" condition, this a ground speed of also 450 kt. This likely will not be the case, and the details of the mid-intercept can easily be adjusted for the prevailing wind conditions.
As a detail, with two aircraft we will likley "stack" them at +/- 2,000 ft flight-level elevations, which will change the details below, slightly. Also, so the "higher" plane is not in the line-of-site of the lower plane, it will "lag" slighly behind in U.T. intercept. A separation of 1 to 2 nautical miles will be sufficient.
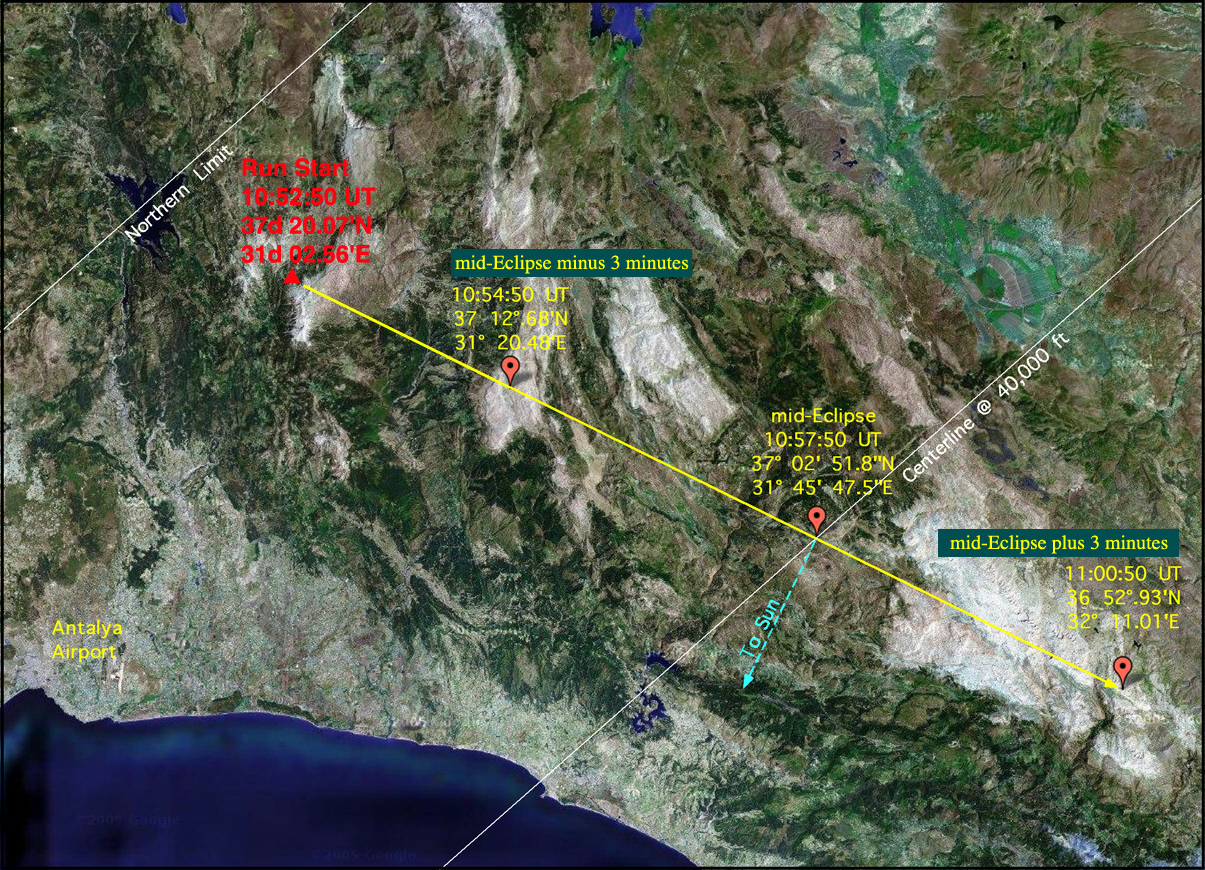
At 10:57:50 U.T. and 40,000 ft flight level, the point of mid-Eclipse intercept is:
Mid-Eclipse Coordinates: 37d 02.86'N, 31d 46.47'E
The azimuth of the Sun at that time is: 206 deg, so the aircraft heading would be 116 degrees.
The run-start position, for this scenario (5 minutes before mid-eclipse) at 10:52:50 U.T is:
Start of totality Run: 37d 20.07'N, 31d 02.56'E
The aircraft CANNOT be late, in arriving at the totality-run start position. The ground-track distance from the Antalya airport is short, only 28.5 nautical miles (53 km), but I presume a nominal rate of climb from T/O, reaching a 40,000 ft flight altitude in 18 minutes (to be confirmed with the flight/aircraft operations crew). The aircraft can arrive "early" at this point and "hold" by maneuvering (circling) to then turn onto the totality-run heading at that position at 10:52:UT. Alternatively, if the aircraft arrives at the position early it can fly parallel to the totality track from that point (at a heading of appx 26.5 deg) and then execute a 90 degree, right, heading realignment at the appropriate difference in time to enable a central mid-umbra intercept further NE along the track. this is easily recomputed in real-time.
In either case duration of appx 30 minutes from an ON TIME takeoff to mid-eclipse would be sufficient with a few "extra" minutes of contingency time built in. The need for an ON TIME take-off is paramount, and must be stressed. Alternatively we would need to build in more contingency time and then "hold" or execute a totality-run further NE along the tract if we takeoff at a planned earlier time.
We will stay on the totality-run track until mid-eclipse + 4 minutes (11:01:50 UT), and then execute a heading alignment maneuver and nominal descent for a landing back at Antalya. That's 75 nautical miles back to Antalya, which we would cover as we descend. Again, I estimate 18 minutes (but might be slightly different).
Hence, the total flight duration would be (about 8 minutes) less than an hour - but we SHOULD plan on some "extra" contingency time on the front end. Not clear if 8 minutes additional contingency minutes is enough.
The details of the baseline "totality run" (to CIII + 3 minutes), as a Quicktime animation, may be seen by clicking on the graphic below. Note, that this specific scenario will result in a duration of totality of 4m 14.4s (appx 25s longer than on the ground at the "same" mid-eclipse location).
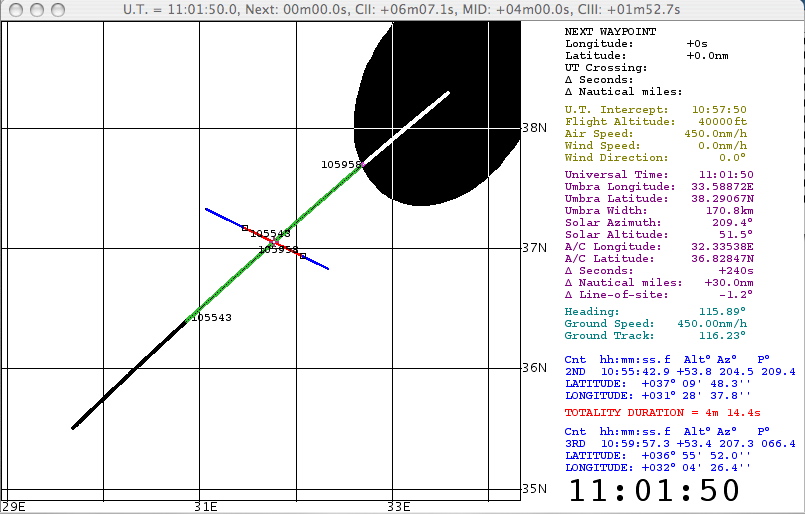
See the EFLIGHT S/W page for explanitory information.
The above scenario (to CIII + 3 minutes) is illustrated below, overlaid on a satellite image of the area:
Return to Glenn Schneider's Home Page
A) Use of Raytheon Hawker-400 jet aircraft or similar:
- Climb to altitude: 18 minutes
- Cruise 450 kt (833 km/hr)
- Service Ceiling: 45,000 ft.
- PAX complement: 8 persons each
- Sunside windows: 5 (sharing necessary)
B) T/O and Landing from Antalya, Turkey (Int'l Airport)
- Lat = 36d 54' N, 30d 48' E
C) Total flight time T/O to Landing = 1 hour
A Eclipse flight "BASELINE" Scenario
Executable, with 40,000 ft observation, in 1 hour flying-time, from/to Antalya airport.
Baseline Scenario for Mid-Eclipse Intercept:
i) Flight Altitude = 40,000 ft*
ii) U.T. of mid-Eclipse Intercept = 10:57:50 U.T.
iii) Cruise speed = 450kt
It must be noted that the altitude of the Sun (angular degrees above the horizon) is 53.6 degrees at this location. This SHOULD be observable out the aircraft windows with some neck craning (but needs to be confirmed), in straight and level flight, BUT it would be highly desirable if the aircraft could be banked (tilted) - while still flying on a fixed heading - by whatever amount may be accommodated to "lower" the sun as seen through the aircraft windows. An intercept point chosen later in time (further to the North East) would have the Sun at a somewhat lower altitude - at the expense of additional flying time. For this baseline scenario, a 10:57:50 UT intercept is considered because of the short flight distance. Clearly, that can be adjusted. Note that 1 minute of flying time (not U.T. intercept)- parallel to the centerline of the path of totality - (after reaching altitude and nominal cruise speed) would move the intercept point by appx 7.5 nautical miles along the path of totality.
The baseline plan assumes a "no wind" condition, this a ground speed of also 450 kt. This likely will not be the case, and the details of the mid-intercept can easily be adjusted for the prevailing wind conditions.
As a detail, with two aircraft we will likley "stack" them at +/- 2,000 ft flight-level elevations, which will change the details below, slightly. Also, so the "higher" plane is not in the line-of-site of the lower plane, it will "lag" slighly behind in U.T. intercept. A separation of 1 to 2 nautical miles will be sufficient.
At 10:57:50 U.T. and 40,000 ft flight level, the point of mid-Eclipse intercept is:
Mid-Eclipse Coordinates: 37d 02.86'N, 31d 46.47'E
The azimuth of the Sun at that time is: 206 deg, so the aircraft heading would be 116 degrees.
The run-start position, for this scenario (5 minutes before mid-eclipse) at 10:52:50 U.T is:
Start of totality Run: 37d 20.07'N, 31d 02.56'E
The aircraft CANNOT be late, in arriving at the totality-run start position. The ground-track distance from the Antalya airport is short, only 28.5 nautical miles (53 km), but I presume a nominal rate of climb from T/O, reaching a 40,000 ft flight altitude in 18 minutes (to be confirmed with the flight/aircraft operations crew). The aircraft can arrive "early" at this point and "hold" by maneuvering (circling) to then turn onto the totality-run heading at that position at 10:52:UT. Alternatively, if the aircraft arrives at the position early it can fly parallel to the totality track from that point (at a heading of appx 26.5 deg) and then execute a 90 degree, right, heading realignment at the appropriate difference in time to enable a central mid-umbra intercept further NE along the track. this is easily recomputed in real-time.
In either case duration of appx 30 minutes from an ON TIME takeoff to mid-eclipse would be sufficient with a few "extra" minutes of contingency time built in. The need for an ON TIME take-off is paramount, and must be stressed. Alternatively we would need to build in more contingency time and then "hold" or execute a totality-run further NE along the tract if we takeoff at a planned earlier time.
We will stay on the totality-run track until mid-eclipse + 4 minutes (11:01:50 UT), and then execute a heading alignment maneuver and nominal descent for a landing back at Antalya. That's 75 nautical miles back to Antalya, which we would cover as we descend. Again, I estimate 18 minutes (but might be slightly different).
Hence, the total flight duration would be (about 8 minutes) less than an hour - but we SHOULD plan on some "extra" contingency time on the front end. Not clear if 8 minutes additional contingency minutes is enough.
The details of the baseline "totality run" (to CIII + 3 minutes), as a Quicktime animation, may be seen by clicking on the graphic below. Note, that this specific scenario will result in a duration of totality of 4m 14.4s (appx 25s longer than on the ground at the "same" mid-eclipse location).

See the EFLIGHT S/W page for explanitory information.
The above scenario (to CIII + 3 minutes) is illustrated below, overlaid on a satellite image of the area:

Return to Glenn Schneider's Home Page